Pedestrianisation concept for the city center of a major metropolis

The metropolitan city is reeling under high levels of pollution and traffic congestion. The city is planning initiatives to make the city more liveable and sustainable. Our client is a major municipal body in the city and seeks to pedestrianise a key area under its jurisdiction and create an extended vehicle free zone. The objective of the project is also to develop the project areas as a benchmark for pedestrian priority zones in the city with limited pedestrian only zones. The project area is a central business district of the city, a shopping and entertainment destination, and includes a major metro rail interchange station. The project area attracts up to 500,000 people per day. The area also plays a key role in the road network of the city since roads in the area connect major zones of the city. This presents a particular challenge in making the area car free. The project also faces significant challenges in terms of stakeholder agreement since the business owners operating in the area have historically opposed the project.
M-Prime was tasked to develop the strategy and the concept design for the pedestrianisation of this key area in the city centre.
The way to problem solvingGiven our extended experience in strategy development and stakeholder management, we used a step-by-step methodology and empirical data to present a case for pedestrianisation of the area, and developed a concept design for developing the implementation plan. Specifically, the key steps included:
- Development of the vision and objectives for the project based on the characteristics of the area such as historical and heritage built structure, art and culture facilities, entertainment and leisure facilities, commercial and shopping facilities, business and financial areas, etc., as well as based on the global benchmarks for areas with similar characteristics
- Identifying key enablers to enhance the character of the area to make it more attractive as a pedestrian only zone. The key enables includes the aspects of aesthetics, placemaking, mobility, safety, accessibility, etc.
- Study of global benchmarks, with similar urban structure and where car free zones have been implemented, to understand the applicability for the project area and identify key learnings and risks
- Review of data from other case studies to understand the impact of pedestrianisation and traffic calming on business
- Study of the ‘as-is’ situation in the project area to understand key characteristics such as existing traffic flows, pedestrian flows, key demand generation areas including public transport stations/stops, magnitude of through traffic, number of parking spaces currently in use, etc.
- Development of the master plan for the pedestrianisation that included two options: one included a limited traffic free area, and the other with a more extended traffic free area, and selection of the preferred option based on the objectives
- Identifying the key measures to implement the exclusive pedestrian zone in the project area. This included identification of five key category of measures such as parking, diversion of traffic, improvements in public transport facilities, improvements in pedestrian facilities and Travel Demand Management, and assessment of each measure against 4 key parameters to identify the suitability of each measure.
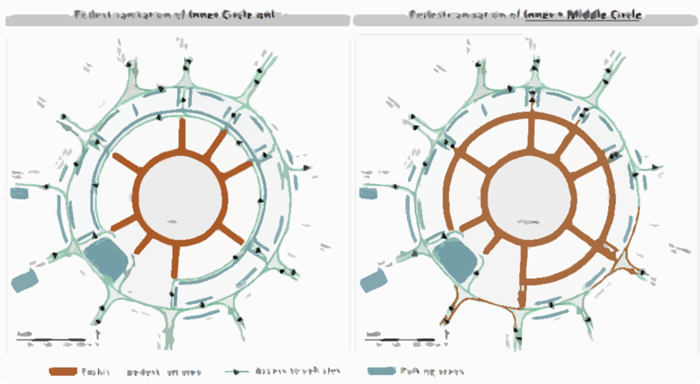
Our work resulted in the development of a strategy and concept design document ready for stakeholder consultation, and provided a skeleton for implementation. Specifically, the key results of the project included:
- development of a platform based on a structured methodology and empirical data to agree vision and objectives among the stakeholders, and to agree enablers that needs to be enhanced for targeted characteristics of an exclusive pedestrian zone
- development of a rational to select with the stakeholders, the extent of the project area
- identification of key measures that include parking restrictions, traffic diversions, enhancement of public transport and pedestrian infrastructure, and require detailed designing for implementation.
Back
